Red Teaming
Mastering blockchain security’s backbone: new Challenge category
Understand how blockchain works and critical security aspects with a set of new, curated Challenges.

b3rt0ll0,
Jun 20
2023
Table of Contents
Part of the Hack The Box (HTB) mission is to provide our community with constantly up-to-date content, following the latest trends and threats. We are now excited to announce the introduction of a new Challenge category focusing on blockchain technology, powered by HackenProof.
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, security has become an increasingly crucial aspect, particularly with the growing popularity of blockchain. With the involvement of a large amount of funds (with a market size value of $11B in 2022 and projected to grow to $469B by 2030) and the potential for significant financial losses, ensuring the robustness and integrity of smart contracts have become fundamental.
This new set of cybersecurity upskilling content will address prominent Web3 concerns and vulnerabilities that affect developers, corporations, and users.
What is blockchain (in a nutshell)
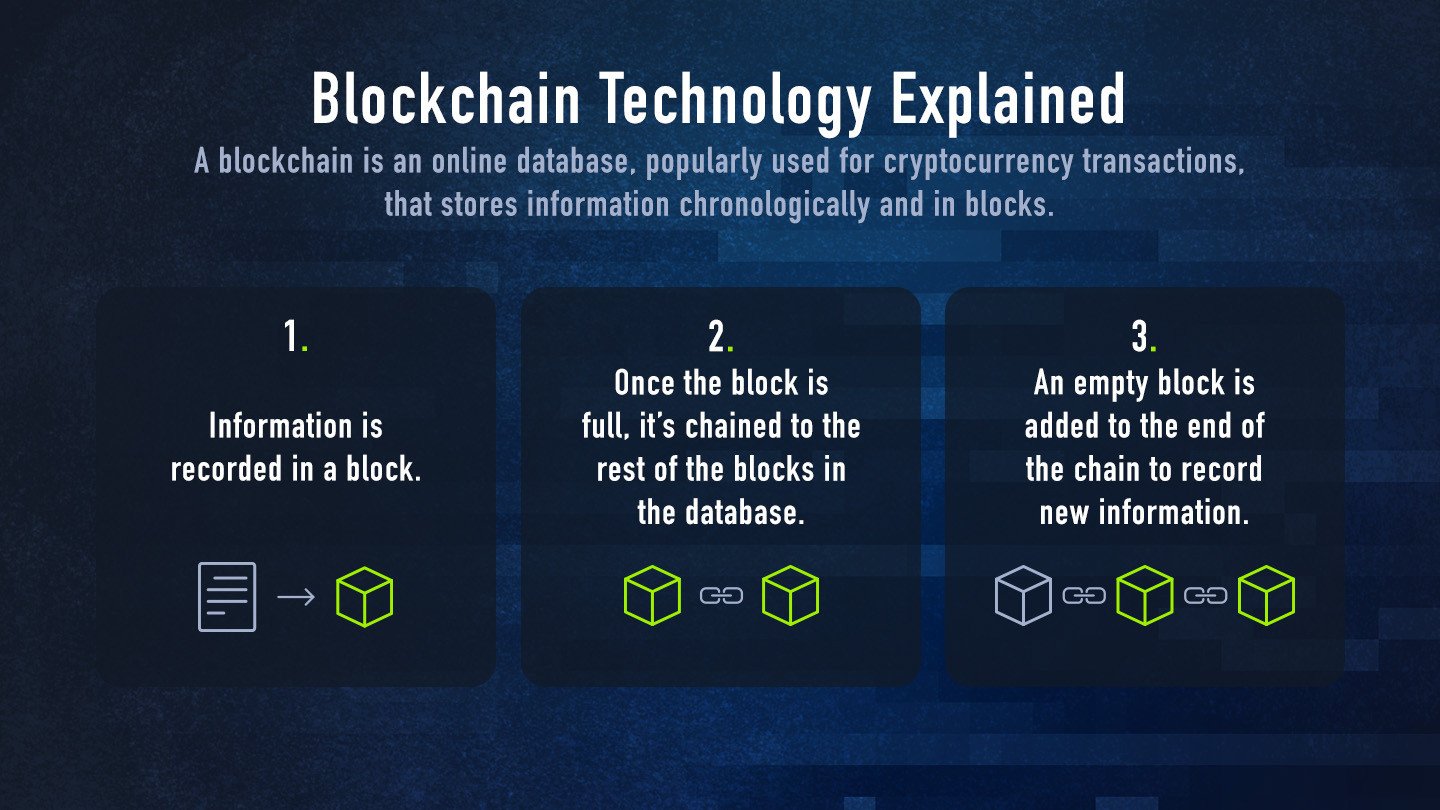
A blockchain, also known as distributed ledger technology, is an online database that’s popularly used for cryptocurrency transactions. The database stores digital information in blocks and in chronological order. Once a block is full, it’s linked and locked to the rest of the full blocks in the database, creating a chain. An empty block is then added to the end of the chain to record new information.
In simpler terms, we can think of blockchain technology as a paper ledger book, which is used to record transactions. Once one page is full, you must flip to the next blank page to continue recording information, and so on. In the case of a blockchain, once a block is filled and locked into the chain, that block can no longer be changed.
One of the most important principles of this technology is the so-called Blockchain Trilemma: security, decentralization, and scalability.
-
Security refers to the integration of a complete risk management system. Trust in transactions is ensured through the core principles of a blockchain security framework, which are consensus, cryptography, and decentralization. There are three main types of blockchains, which can be categorized into (1) Private, (2) Public, and (3) Consortium.
-
Decentralization refers to the dispersion of supervision and decision-making power from a central governing body to individual entities. Every new transaction that takes place requires verification before creating its block and adding it to the chain. The decentralized system makes sure that control over the blockchain is distributed across each individual, not in the hands of a specific group or individual.
-
Scalability refers to the ability of a blockchain network to manage a high number of transactions by increasing the number of nodes on the platform. Transparency and security are the two major benefits of blockchain scalability.
Blockchain technology has significantly changed the way in which traditional networks operate, as it is based on the concepts of cryptography and decentralization. Taking an overall look, these characteristics provide many security benefits.
The misconception, however, is to think of blockchain as fully secure by default.
Introduction to blockchain security
The question should not be “is it possible to hack the blockchain?” but more a “what vulnerabilities could exist, and how can they be exploited?”
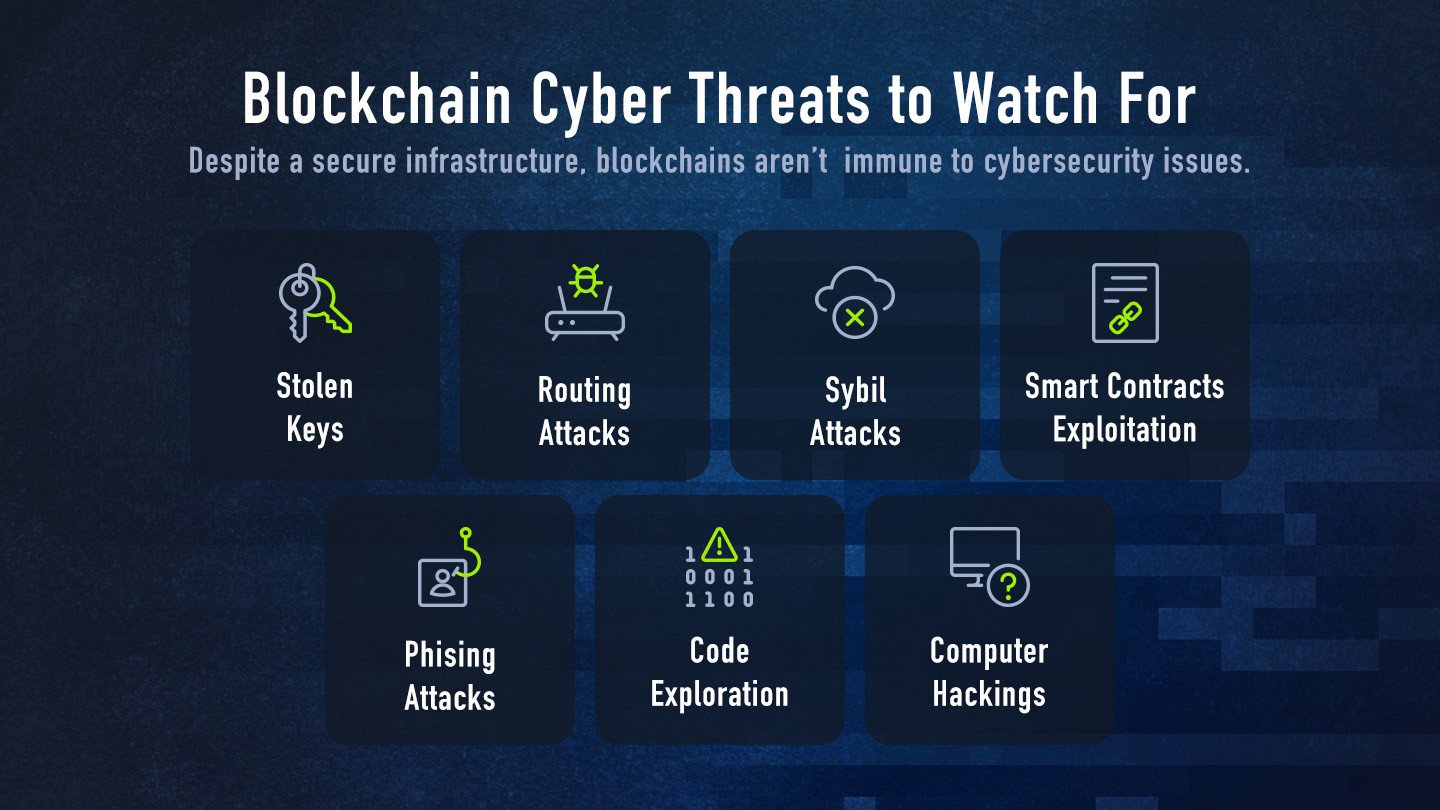
Looking at historical data, and some impressive real-world examples, consider the following cyber threats when interacting with blockchain technology.
-
Stolen keys: as mentioned, every blockchain user is granted a unique identifier to enter the network. Well, this can be stolen! In 2021, $140 million worth of Bitcoin was stolen from crypto users. Authorities pointed to stolen keys as the source of the theft.
-
Routing attacks: they can come in a few forms, the most common being denial of service attacks and man-in-the- middle attacks. In both cases, data can be intercepted and transferred across a network, usually a weak Wi-Fi network.
-
Sybil attacks: these happen when a network is overwhelmed with login attempts or false credentials, which causes a temporary crash and the network becomes compromised.
-
Phishing attacks: One of the oldest hacking attempts in the book. Phishing messages might entice blockchain users to provide their unique ID associated with a blockchain account or encourage them to click a link that gains access to a blockchain network. In November 2022, a crypto scammer managed to steal $800,000 in NFTs.
-
Employee computer hacked: particularly relevant for corporations. When Bithumb was hacked, $870,000 were stolen, and more than 30,000 users' data were compromised. The root problem came from an employee’s computer, raising questions about the security of the entire industry.
-
Code exploration: when a blockchain user identifies a weak spot in a blockchain’s software and exploits that weakness in the underline blockchain implementation with malicious intent. In 2016, more than $50 million were swiped from a venture capital fund known as a decentralized autonomous organization by way of code exploitation.
-
Smart contracts exploitation: over $1.2B worth of crypto-assets (only $154 million in the same period of 2021) were stolen in the first quarter of 2022 this year alone. The need for cybersecurity professionals to help protect smart contracts has never been higher.
Smart contracts and Web3 bug bounty hunting
In our article introducing the concept of bug bounty hunting, we have mentioned an impressive payout of $2M for a vulnerability identified on Polygon network and reported to have been at risk of $850M in case of exploitation.
Given the high amount of funds and increased popularity of the industry, the crypto bug bounty space has improved greatly in the last couple of years, with white hat hackers receiving adequate payouts for securing protocols. Along with the main bug bounty platforms like HackerOne, Synack, and Bugcrowd, other specialized communities have emerged, such as HackenProof and Immunefi, to fight DeFi (decentralized finance) hacks responsible for more than $10B in losses.
Smart contracts
Smart contracts are simply programs stored and executed in the blockchain. They are typically used to automate the execution of an agreement so that all participants can be immediately certain of the outcome, without any intermediary’s involvement or time loss. Usually, smart contracts are:
-
Fast, efficient, and accurate
-
Trustworthy
-
Transparent
-
Secure (most of the time…)
Why smart contracts attacks?
The answer is very simple: money. In the case of smart contracts, a single mistake in a smart contract could lead to the irreversible theft of millions of dollars. Smart contracts are excellent targets due to their ability to hold high-value crypto-assets, and with the complex smart contract code usually being immutable, it may take just one error to compromise the entire protocol.
Practice on Hack The Box
To address this industry need, we have developed a comprehensive set of Challenges aimed at transforming inexperienced developers into highly skilled individuals proficient in understanding the underlying technology of smart contracts and the associated security challenges.
The content encompasses a wide range of well-known smart contract vulnerabilities, participants will not only gain practical expertise in smart contract security, but they will also develop a comprehensive understanding of the broader implications and potential vulnerabilities associated with blockchain-based systems.
Embark on an epic and fully gamified 8-bit RPG adventure alongside Alex, where you'll be transported to a world teeming with mythical creatures and endless possibilities. Prepare yourself for the adventure of a lifetime, where courage and determination will be your greatest allies.
The Challenges will be gradually released and available to all our community members. Here is what to expect:

Blockchain security for enterprise
Organizations can employ experts to help you design a compliant and secure solution and help you achieve your business goals, or upskill talent in-house.
When building an enterprise blockchain application, it’s important to consider security at all layers of the technology stack, and how to manage governance and permissions for the network. A comprehensive security strategy for an enterprise blockchain solution includes using traditional security controls and technology-unique controls.
The new set of blockchain Challenges will soon be available for business customers too, enabling major organizations to act safely and protect millions of funds. Get in touch with our team to know more.















