Cyber Teams
How to apply the MITRE ATT&CK framework to your cybersecurity strategy
The MITRE ATT&CK framework is a knowledge base of cyber attacks based on real-world attack scenarios. Learn how to apply this to your cybersecurity strategy in our guide.

Howard Poston,
Jul 17
2024
Table of Contents
What is the MITRE ATT&CK framework?
The MITRE ATT&CK framework is a knowledge base of cyber attacks based on real-world attack scenarios. It breaks a cyber attack into high-level objectives, called Tactics, and identifies the various Techniques used to achieve them.
-
Tactics: The high-level goals that attackers want to achieve at different stages of an attack. Examples include Reconnaissance, Execution, and Defense Evasion.
-
Techniques: Describe the "how" behind a tactic. For example, the Reconnaissance Tactic has concrete steps with techniques like Active Scanning, Vulnerability Scanning, Gather Victim Identity Information, etc.
MITRE Corporation designed the framework to provide insight into the stages of a cyber attack and create a common language for how an attacker can achieve their goals.
The most commonly used MITRE ATT&CK framework is the Enterprise framework, but there are also ATT&CK matrices for mobile devices and industrial control systems (ICS) as well.
MITRE ATT&CK provides a wealth of information about the anatomy of a cyber attack.
In addition to describing the various offensive techniques an attacker may use, it also outlines methods that organizations can use to detect, prevent, or mitigate these techniques.
MITRE ATT&CK can be invaluable for developing defenses, planning penetration tests, and understanding the capabilities of a particular threat actor, attack campaign, or malware variant.
MITRE ATT&CK Tactics and Techniques
The MITRE ATT&CK framework is organized around Tactics that describe an attacker’s key tasks or goals. These Tactics include:

-
Reconnaissance: Exploring the target and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
-
Resource Development: Developing C2 infrastructure, malware, or other resources to support attacks.
-
Initial Access: Gaining an initial foothold on target systems.
-
Execution: Running malware on an infected system.
-
Persistence: Protecting the attacker’s foothold against restarts, etc.
-
Privilege Escalation: Gaining higher-level permissions on an infected machine.
-
Defense Evasion: Defending against antivirus and other security solutions.
-
Credential Access: Stealing passwords, API keys, SSH keys, etc.
-
Discovery: Exploring an infected network from the inside.
-
Lateral Movement: Moving from one system to another within a network.
-
Collection: Collecting sensitive and useful data from compromised systems.
-
Command and Control: Communicating between malware and its operator.
-
Exfiltration: Moving data out of the infected network.
-
Impact: Attacking system confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
Under each of these Tactics are a number of Techniques and Sub-Techniques used to achieve these goals. In total, MITRE has over 200 Techniques and over 450 Sub-Techniques.
Organizations have the need to develop threat models, evaluate security tool efficacy, develop detection strategies, and prioritize security investments. For this reason, we carefully mapped our courses and labs to the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Managers using the HTB Enterprise Platform can easily search courses using MITRE terminology and assign them based on the techniques and tactics relevant to their teams.
This search feature works with specific MITRE tactics or techniques (for example, T1594 or Active Scanning) or with text keywords found in the course material.
6 reasons to map your security strategy to MITRE ATT&CK
The MITRE ATT&CK framework provides a massive amount of information in a well-organized and digestible format. The framework can be adapted and applied to various security tasks, including:
1.Improved security coverage: MITRE ATT&CK attempts to cover every known way that a threat actor could achieve various goals in the cyber attack lifecycle. Mapping security infrastructure and controls to MITRE ATT&CK therefore helps an organization pre-emptively identify and remediate any gaps.
💡 Easi, a European IT services partner with over 400 employees, successfully implemented a skills development program that directly applies to engagements with clients. The mapping of HTB Professional Labs to the MITRE ATT&CK matrix made it much easier to keep the training sessions aligned to real-world scenarios.
2. Strategic planning: Make it harder to conduct Reconnaissance of your network, and you reduce the Impact an adversary can have.
For a cyber attack to succeed, an attacker needs to move successfully from the Reconnaissance phase to Impact. While some stages may be optional, others are essential.
By mapping security strategies to MITRE ATT&CK, an organization can identify potential chokepoints where internal teams can focus resources and maximize the chances of successfully detecting and blocking an attempted attack.
Make it harder to conduct Reconnaissance of your network, and you reduce the Impact an adversary can have.
3. Enhanced incident response: MITRE ATT&CK describes both how various attacks work and how to detect and mitigate them.
Having a clear understanding of the ATT&CK framework can help defenders understand where to look for indicators of attack (IoAs), which helps expedite incident detection and response.
4. Security testing: Penetration tests rarely have the time or resources necessary to comprehensively evaluate an organization’s security architecture against every possible threat.
Using MITRE ATT&CK, organizations can identify the techniques that they are most likely to face, and where to focus penetration testing to provide the most return on investment.
5. Enriched threat intelligence: Many security resources map threat actors and malware to the ATT&CK framework. In fact, MITRE includes a list of APTs and their known tools and techniques.
Combining MITRE ATT&CK with threat intelligence provides insight into how an organization is best positioned to detect and manage a documented or emerging threat.
6. Regulatory compliance: Data protection regulations such as GDPR, PCI DSS, and HIPAA mandate that organizations have controls in place to prevent unauthorized access, data exfiltration, and similar threats.
Mapping defenses to MITRE ATT&CK helps with gap identification and provides security leaders with the confidence needed to assert compliance with regulatory requirements.
Practical MITRE ATT&CK framework use cases
The MITRE ATT&CK framework contains an ocean of information on how cyber attacks work and how defenses should be designed to address them.
Its breadth of coverage means that there are many ways to apply it to address business needs. Review the following use cases to determine which works best for your organization and its risk management priorities.
Security gap and risk assessment
The MITRE ATT&CK framework attempts to comprehensively identify all of the potential means that an attacker can achieve various stages of the cyber attack lifecycle.
The greater an organization’s visibility into and coverage of these attack vectors, the higher the probability it can prevent or quickly remediate an identified threat.
Organizations can use the MITRE ATT&CK framework as a guide for developing their security architecture.
For example, most attackers’ initial foothold on a corporate network—typically user workstations—is not the same as their final destination—often database servers or other repositories of high-value data. Getting from A to B means moving laterally through a compromised network.
A company designing defenses against this could benefit from a review of the Lateral Movement Tactic in the ATT&CK framework. This details the various ways that intruders move through the network and how to detect and mitigate these techniques.
The Detection and Mitigation sections under these Techniques can be used as a checklist for designing security controls to manage this threat. And, once a company has implemented and tested these new controls, it can move on to the next threat on its list or column in the ATT&CK matrix.
Security analyst training/incident detection
Having the right security solutions is important, but corporate SOC teams also need to know how to operate them.
The ability to quickly differentiate between a true threat and a false positive is essential to prevent analysts from being overwhelmed by high alert volumes and to minimize the cost of an intrusion on the business.
The MITRE ATT&CK framework describes various threats and how to detect and mitigate them.
After identifying key areas your SOC team needs training on, provide them with resources to learn those skills.
For example, HTB provides the resources that companies need to train these analysts in vital skills. Many HTB resources—including HTB CTFs—are mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Note:💡HTB Enterprise users can even search for a particular Technique using ATT&CK terminology to identify resources for upskilling their analysts on these threats. For a good starting point, check out HTB’s Orion Lab, an Enterprise-exclusive Lab with extensive ATT&CK coverage and mappings.
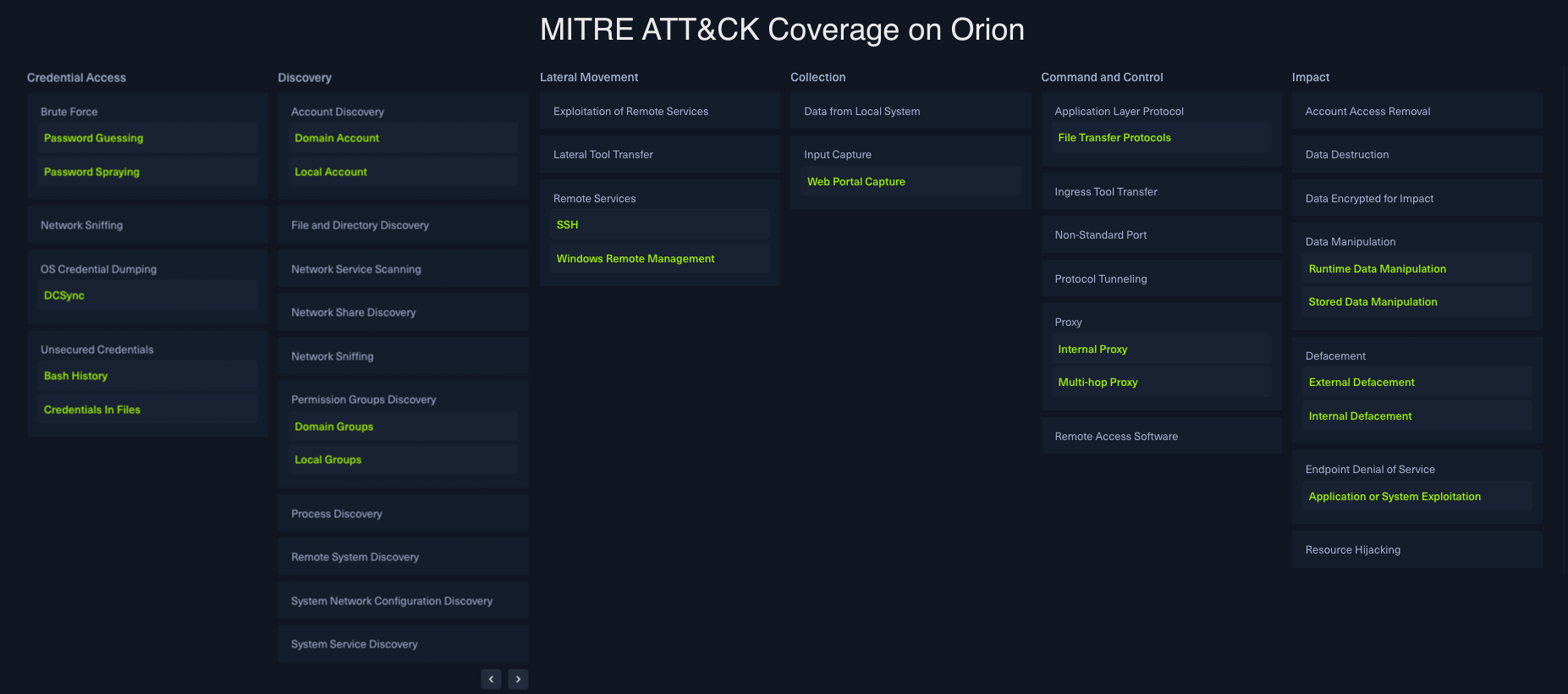
(MITRE ATT&CK coverage on Orion Professional Labs)
Targeted security testing
The goal of security testing is to decrease the organization’s exposure to cybersecurity risk to the greatest extent possible. The best way to do this is to look for vulnerability to the threats that an organization is most likely to face.
For insight into what these threats may be, an organization can look to threat intelligence and MITRE ATT&CK. These provide insight into the types of attacks that other organizations in the same industry or sector, or country or jurisdiction, face and the tools and techniques used by major threat groups. Based on this research, an organization may decide to focus security testing on its web applications, remote work infrastructure, cloud footprint, or other areas.
With a defined focus, the company can use MITRE ATT&CK and HTB to build the skills necessary to accurately assess their vulnerability to a particular threat.
With ATT&CK, the company can define the various ways to accomplish a particular attack. Then, HTB’s mappings to MITRE ATT&CK and Enterprise ATT&CK search capabilities enable companies to build tailored training paths to build employee capabilities in key areas.
For example, your organization likely has defenses in place to identify attempted exfiltration of customer data, IP, and other sensitive data from the corporate network.
ATT&CK’s Exfiltration Tactic details all of the means by which an attacker can achieve this, and HTB provides hands-on training on how to perform, or defend against, many of the techniques.
With skills learned from HTB, your analysts can test whether existing controls actually protect against data exfiltration or provide a false sense of security.
Understanding emerging threats
When security researchers write articles about emerging threats, they commonly map them to the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
MITRE ATT&CK provides a common terminology and makes it easier for organizations to determine whether they have the capability in place to identify and pre-emptively address a particular threat.
Because there’s a huge difference between:
-
Knowing that a malware sample uses process injection
-
Understanding how process injection works, the warning signs of it, and how to detect and mitigate it.
For this, the MITRE ATT&CK framework provides more information about the individual attacks and tactics that a threat actor may use.
After identifying threats that your organization may be vulnerable to, research how those threats work, and how you can stop them before they become a problem.
Additionally, HTB provides the tools needed to close this gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world experience.
When digging into an emerging threat, security analysts can search for the relevant MITRE ATT&CK Techniques in HTB and gain experience in how the attack actually works.
This can be invaluable for both defining defenses and testing their effectiveness.
💡For an example of how this works, check out our recent post on Cuttlefish malware.
We break down the key capabilities of the malware and map them to MITRE ATT&CK Techniques. Then, we point out HTB resources that can be used to learn more about those Techniques and how they actually work.

Regulatory compliance and governance, risk, and compliance (GRC)
Regulatory requirements include more than just the security controls that a company has in place. Often, they mandate security training as well.
This ranges from requiring standard cybersecurity awareness training, such as phishing or malware training, to the NIS2 directive that corporate management “oversee, approve, and be trained on the entity’s cybersecurity measures and to address cyber risks.”
The MITRE ATTC&K framework can provide structure for this cybersecurity training by identifying and describing the various risks that an organization may face and how to manage them.
Operationalizing MITRE ATT&CK frameworks
At the end of the day, MITRE ATT&CK is just a resource. It can be incredibly helpful if used correctly, but it doesn’t do anything to help the business on its own.
To take advantage of the ATT&CK framework, try identifying one area of the business where full visibility into how cybercriminals do their jobs would be useful (defense development, pen test planning, etc.). Identify a use case, test it out, and build from there.













